Top Types of Wall Cladding Panels for Modern Architecture?
In modern architecture, aesthetic appeal and durability are priorities. Wall cladding panels play a critical role in achieving both. These panels enhance the visual appeal of structures while protecting them from external elements.
Various materials are available for wall cladding panels, including wood, metal, and composite options. Each material offers unique benefits and challenges. For example, wood gives a warm and natural look but may require more maintenance. Metal, on the other hand, is modern but can be costly. Composite materials balance the two, yet they may lack authenticity.
Choosing the right wall cladding panels is not always straightforward. Architects and builders face tough decisions as they weigh aesthetics against functionality. Reflecting on this choice can reveal personal biases. Balancing personal taste with structural integrity is essential. The evolving landscape of materials encourages ongoing exploration and innovation.

Types of Materials Used for Wall Cladding Panels in Modern Architecture
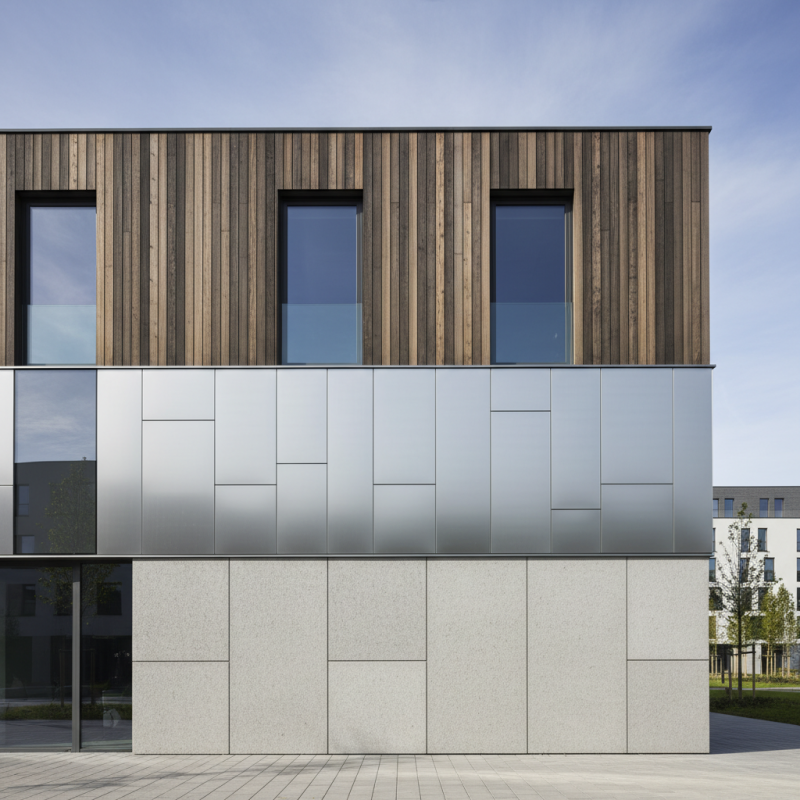
Wall cladding panels play a vital role in modern architecture. They offer both aesthetics and functionality. The materials used for these panels are diverse. Each type brings its own charm and challenges.
Wood is a classic choice for wall cladding. It adds warmth and character to buildings. However, it requires regular maintenance. Without proper care, wood can warp or fade. Metal panels, like aluminum, provide a sleek, industrial look. They are durable and weather-resistant. Yet, they can be prone to dents and scratches.
Another popular option is composite materials. These panels combine different substances for enhanced performance. They often mimic the appearance of wood or stone. Still, they might not always match the naturalness of these materials. Lastly, stone cladding offers a timeless appeal. Its robust nature is unmatched, but installation can be complex and costly. Each material has its strengths and weaknesses. The choice largely depends on the specific vision of the architect.
Top Types of Wall Cladding Panels for Modern Architecture
| Material Type | Key Characteristics | Advantages | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vinyl | Lightweight, durable, and low-maintenance | Cost-effective, resistant to moisture and insects | Residential exteriors, commercial buildings |
| Wood | Natural appearance, versatile in design | Aesthetic appeal, good insulation properties | Cottages, modern homes, and restaurants |
| Metal | Strong, durable, and often lightweight | Fire-resistant, low maintenance, various finishes | Commercial structures, industrial buildings |
| Stone | Natural, unique appearance, long-lasting | High durability, excellent thermal mass | High-end residential and commercial buildings |
| Concrete | Versatile, strong, and highly durable | Energy-efficient, soundproof, fire-resistant | Modern homes, urban buildings, and offices |
Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Wall Cladding Options
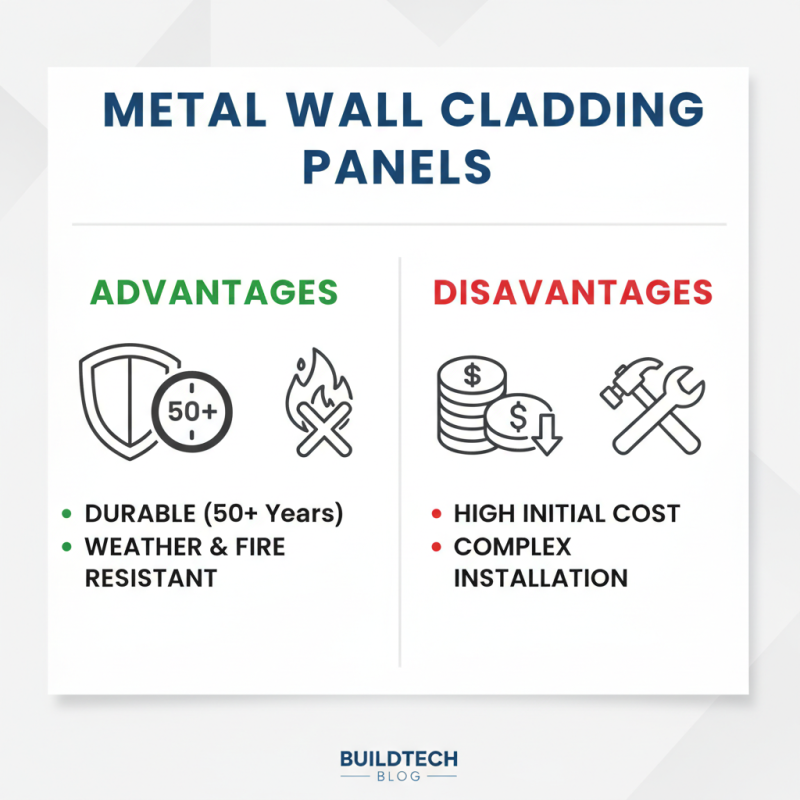
When choosing wall cladding panels, it's essential to understand both the advantages and disadvantages of various options. For instance, metal cladding offers durability and sleek aesthetics. According to a report by the Metal Construction Association, metal panels can last over 50 years with minimal maintenance. They resist weather damage and are fire-resistant. However, their initial cost can be quite high. Installing metal cladding might strain tight budgets.
On the other hand, wood cladding presents a warm, organic feel. This can enhance the appeal of modern architecture. A study from the Forest Products Laboratory shows treated wood can last up to 30 years. Yet, it requires regular maintenance to prevent rot and insect damage. Environmental factors can heavily influence its longevity. Some might argue that wood's aesthetic is often worth the extra upkeep.
Vinyl cladding is another popular choice. It’s cost-effective and available in various styles. Research from the Vinyl Siding Institute shows that homes with vinyl siding can see an increase in resale value. However, it might not withstand extreme weather conditions well. Over time, fading is a concern. The balance between cost, maintenance, and durability is essential when selecting the right wall cladding.
Popular Styles and Finishes of Wall Cladding Panels for Contemporary Design
Wall cladding panels are essential in contemporary architecture. They not only serve a functional purpose but also enhance aesthetics. A report by Research and Markets predicts that the wall cladding market will reach $255 billion by 2027, driven by the demand for modern designs.
Among popular styles, wood and metal cladding stand out. Wood panels offer warmth and texture, creating a cozy atmosphere. However, they may require more maintenance due to weathering. Metal cladding, on the other hand, provides a sleek look, but it can be prone to denting or scratches. The choice between these styles often reflects personal taste and location.
Moreover, finishes play a significant role in wall cladding. Textured finishes can add depth to a building's facade. Smooth finishes create a modern vibe but may show imperfections more easily. Each finish has pros and cons, and the best choice often demands careful consideration and sometimes experimentation. Modern architecture thrives on creativity, yet it is crucial to balance aesthetics with practicality.
Top Types of Wall Cladding Panels for Modern Architecture
This chart displays the popularity of various types of wall cladding panels used in contemporary architecture. The data reflects the increasing trends based on usage in recent design projects.
Sustainability Considerations in Selecting Wall Cladding Materials
Sustainability is a key factor in selecting wall cladding materials. Many architects prioritize eco-friendly options that reduce environmental impact. Recycled materials are increasingly popular. They require less energy for production and contribute to waste reduction. For example, reclaimed wood adds character and reduces the need for new resources.
Natural stone is another sustainable choice. It offers durability and requires minimal maintenance. However, sourcing can impact its sustainability. Some stones may be harvested unsustainably, leading to ecological damage. This factor requires careful consideration. Lightweight panels, often made from composite materials, can also be sustainable. They are often produced using recycled components, but their lifespan and recyclability vary.
Even with these options, challenges remain. Some materials may not be fully biodegradable or can emit VOCs. It's essential to research life cycles, from production to disposal. Choosing cladding should involve understanding its long-term effects on the environment. Aesthetic appeal and sustainability can coexist, but one shouldn't overshadow the other. Balancing both aspects often leads to reflection and mindful choices.
Installation Techniques and Maintenance Tips for Wall Cladding Panels
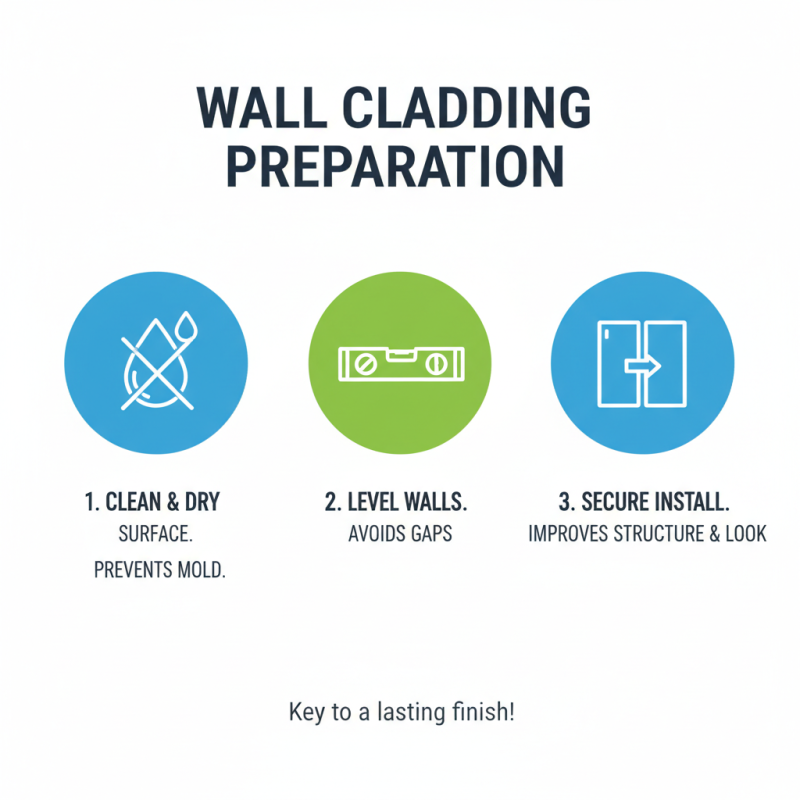
When installing wall cladding panels, proper preparation is key. Start by ensuring the surface is clean and dry. Any moisture can lead to mold growth later. Use a level to check the walls. An uneven surface can result in gaps. These gaps not only affect aesthetics but can also cause structural issues over time.
For the actual installation, use adhesive or fasteners depending on the panel material. Alignment is crucial; misaligned panels will look unprofessional. Ensure you allow for expansion gaps, especially in areas with temperature variations. After installation, routine maintenance is vital. Regular cleaning helps avoid buildup that could damage the surface.
Inspect panels for any signs of wear or damage. Addressing these issues early is important. Small cracks can develop into larger problems. If you notice peeling or fading, it may be time for a refresh. Remember, maintenance is not just about aesthetics. It also preserves the longevity of your investment.
Related Posts
-

What is Building Cladding Panels and Why Are They Essential for Construction
-

Transform Your Space: The Ultimate Guide to Choosing PVC Wall Cladding for Modern Interiors
-

How to Build Insulated Building Panels for Your Home Construction Project
-

2026 Top Building Panels Trends and Innovations to Watch?
-
2026 How to Choose the Right Composite Cladding for Your Home?
-

What is the Importance of Building Panels in Modern Construction?